Question 12.5: A 3500 hp induction motor is started in a system configurati......
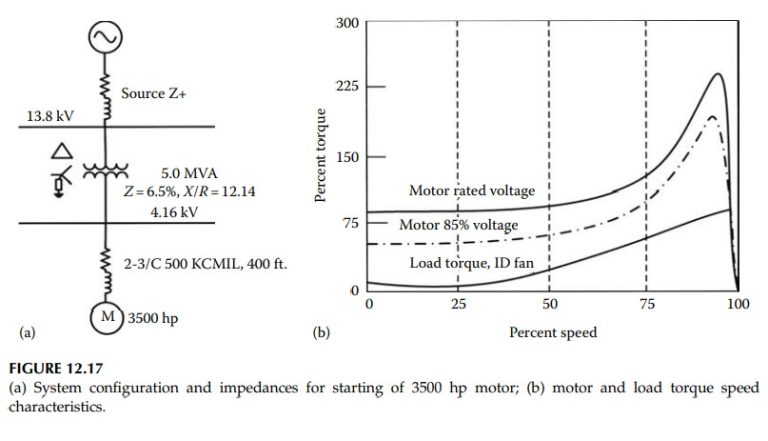
A 3500 hp induction motor is started in a system configuration as shown in Figure 12.17a.
Learn more on how do we answer questions.
The only load on the transformer secondary is the 3500 hp motor. This is a typical starting arrangement for large motors. While a motor connected to a dedicated transformer may be able to tolerate and accelerate its load, the other loads if connected to the same bus may shut down or experience unacceptable voltage dips during starting. The motor is four-pole, rated voltage 4 kV, and has a full load power factor of 92.89%, efficiency = 94.23%, and full load current is 430.4 A. Again the motor rated voltage is slightly lower than the rated bus voltage of 4.16 kV. The locked rotor current is 576% at 19.47% power factor. This gives a starting impact of 3.344 MW, 17.35 Mvar, equivalent to 17.67 MVA. This starting impact is calculated at rated voltage. As the starting impact load is a constant impedance load, if the starting voltage is lower the starting impact load will reduce proportionally. The transformer is rated 5.00 MVA. Short-term loading of the transformer is acceptable, but if more frequent starts are required, the transformer rating must be carefully considered. The 5 MVA transformer of 6.5% impedance can take a three-phase short-circuit current of 12.3 kA for 2 s according to ANSI/IEEE [18] and also NEMA [8] allows two starts per hour, one with the motor at ambient temperature and the other when the motor has attained its operating temperature.
The motor torque speed characteristics, power factor, and slip are shown in Figure 12.17b. It has a locked rotor torque of 88.17% and breakdown torque of 244.5% at rated voltage. The standard load inertial according to NEMA for this size of motor is 8700 lb-ft² . The motor drives a boiler ID (Induced Draft) fan of twice the NEMA inertia = 17400 lb-ft² (H = 4.536). To this must be added the inertia of the motor and coupling, say the total load inertia is 19790 lb-ft² (H = 5.16). The speed torque curve of the load is shown in Figure 12.17b. For a dynamic motor starting study this data must be obtained from the manufacturer.
The system configuration shown in Figure 12.17a has a source impedance (positive sequence) of 0.166 + j0.249 ohm. The transformer has an impedance of 6.5%, X/R = 12.14 and the motor is connected through two cables in parallel per phase of 350 KCMIL, 400 ft long.
The starting current, slip, and motor terminal voltage are shown in Figure 12.18b. It is seen that there is a starting voltage dip of 16% and the starting current is reduced approximately proportional to the voltage dip. The voltage dip is shown based upon the rated motor voltage of 4 kV. The motor takes approximately 22 s to start. It is not unusual to see a starting time of 40–50 s for boiler ID fan motors. Figure 12.18a shows the starting torque, the load torque, and the accelerating torque, and Figure 12.18c shows the active and reactive power drawn by the motor during starting.

