Draw the output voltage for the RL differentiator in Figure 20-43.
Question 20.9: Draw the output voltage for the RL differentiator in Figure ...

The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
First, calculate the time constant,
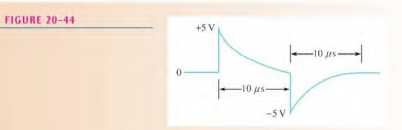
\tau = \frac{L}{R}= \frac{200 \ \mu H}{100 \ \Omega } = 2 \ \mu sIn this case, t_{W}= 5 \tau , so the output will decay to zero at the end of the pulse. On the rising edge, the inductor voltage jumps to +5 V and then decays exponentially to zero. It reaches approximately zero at the instant of the falling edge. On the falling edge of the input, the inductor voltage jumps to —5 V and then goes back to zero. The output waveform is shown in Figure 20-44.
Related Answered Questions
Calculate the time constant.
\tau =RC= (2.2...
First, calculate the circuit time constant.
[latex...
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau =R...
The circuit time constant is
\tau = \frac{L...
The inductor charges through the 30 Ω source resis...
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau = ...
f_{h}= \frac{0.35}{t_{r}}= \frac{0.35}{10\t...
(a) The circuit time constant is
\tau =RC= ...
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau =R...
Calculate the time constant.
\tau = \frac{L...