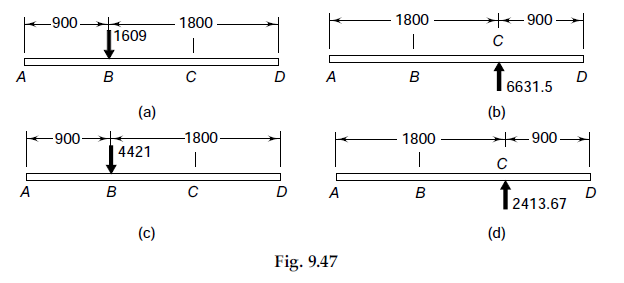
Consider the forces acting on the intermediate shaft of a gearbox illustrated in Example 9.4. The maximum permissible radial deflection at any gear is limited to 1 mm. The modulus of elasticity of the shaft material is 207000 N/mm². Determine the shaft diameter and compare it with the solution of Example 9.4.
Table 9.4 Bending moment and deflection of beams
 |
Case 1 Cantilever Beam – End load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } O=-P l. (1). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=-P(l-x) . (2). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{P x^{2}}{6 E I}(x-3 l) (3). \delta_{\max .} \text { at }(x=l)=-\frac{P l^{3}}{3 E I} (4). |
 |
Case 2 Cantilever Beam—Uniformly distributed load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } O=-\frac{w l^{2}}{2} (5). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=-\frac{w(l-x)^{2}}{2} (6). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{w x^{2}}{24 E I}\left(4 l x-x^{2}-6 l^{2}\right) (7). \delta_{\max .} \text { at }(x=l)=-\frac{w l^{4}}{8 E I} (8). |
 |
Case 3 Cantilever Beam—Moment load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } O=\left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\left(M_{b}\right)_{B} (9). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B} x^{2}}{2 E I} (10). \delta_{\max .} \text { at }(x=l)=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B} l^{2}}{2 E I} (11). |
 |
Case 4 Simply supported beam—Centre load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{P x}{2} (12). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{P(l-x)}{2} \quad(x>1 / 2) (13). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } B=\frac{P l}{4} (14). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{P x\left(4 x^{2}-3 l^{2}\right)}{48 E I} \quad(0<x<1 / 2) (15). \delta_{\max .} \text { at } B=-\frac{P l^{3}}{48 E I} (16). |
 |
Case 5 Simply supported Beam—Uniformly distributed load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{w x(l-x)}{2} (17). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } l / 2=\frac{w l^{2}}{8} (18). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{w x\left(2 l x^{2}-x^{3}-l^{3}\right)}{24 E I} (19) \delta_{\max .} \text { at } l / 2=-\frac{5 w l^{4}}{384 E I} (20). |
 |
Case 6 Simply supported beam—Moment load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B} x}{l}(0<x<a) (21). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B}(x-l)}{l}(a<x<l) (22). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B} x\left(x^{2}+3 a^{2}-6 a l+2 l^{2}\right)}{6 E I l} \quad(0<x< a ) (23). \delta \text { at } x=\frac{\left(M_{b}\right)_{B}\left[x^{3}-3 l x^{2}+x\left(2 l^{2}+3 a^{2}\right)-3 a^{2} l\right]}{6 E I l} (a < x < l) (24). |
 |
Case 7 Simply supported Beam—Intermediate load (A) Bending moment \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{P b x}{l} \quad(0<x<a) (25). \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=\frac{P a(l-x)}{l} \quad( a <x<l) (26). (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{P b x\left(x^{2}+b^{2}-l^{2}\right)}{6 E I l} \quad(0<x<a) (27). \delta \text { at } x=\frac{P a(l-x)\left(x^{2}+a^{2}-2 l x\right)}{6 E I l}(a<x<l) (28). |
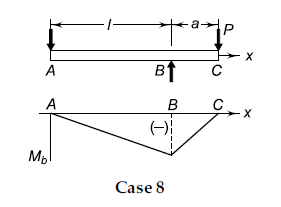 |
Case 8 Simply supported beam—Overhang load (A) Bending moments \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=-\frac{P a x}{l} \quad(x<l) . (29) \left(M_{b}\right) \text { at } x=P(x-l-a) \quad(x>l) (30) (B) Deflections \delta \text { at } x=\frac{\operatorname{Pax}\left(l^{2}-x^{2}\right)}{6 E I l} \quad(x<l) (31). \delta \text { at } x=\frac{P(x-l)\left[(x-l)^{2}-a(3 x-l)\right]}{6 E I} \quad(x>l) (32). \delta \text { at } C=-\frac{P a^{2}(l+a)}{3 E I} (33). |