Question 12.1: To which family of organic compounds do the following compou...
To which family of organic compounds do the following compounds belong? Explain.
(a) \begin{array}{r c}\underset{|}{H}\ \quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \; \underset{|}{H}\quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \quad \\ H-C-C=C-C-H \\\quad \quad\quad \quad\overset{|}{H}\quad\quad \quad\quad\quad\;\overset{|}{H} \quad \quad \end{array} (b) \begin{array}{r c}\underset{|}{H}\ \quad \underset{|}{H}\quad\underset{|}{H}\quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \quad \\ H-C-C-C-C-H \\\quad \quad\quad \quad\overset{|}{H}\quad \; \overset{|}{H} \quad \overset{|}{O} \quad \; \overset{|}{H} \qquad \\ \overset{|}{H} \qquad \qquad \end{array}
(c)  (d) \begin{array}{r c}\underset{|}{H}\ \quad \underset{|}{H}\qquad \quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \quad \\ H-C-C-C-C-C-H \\\quad \quad\quad \quad\overset{|}{H}\quad \overset{|}{H}\quad \; \overset{||}{O}\quad \; \overset{|}{H} \quad \overset{|}{H} \quad \quad \end{array}
(d) \begin{array}{r c}\underset{|}{H}\ \quad \underset{|}{H}\qquad \quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \underset{|}{H}\quad \quad \\ H-C-C-C-C-C-H \\\quad \quad\quad \quad\overset{|}{H}\quad \overset{|}{H}\quad \; \overset{||}{O}\quad \; \overset{|}{H} \quad \overset{|}{H} \quad \quad \end{array}
ANALYSIS Identify each functional group from the list in Table 12.1, and name the corresponding family to which the compound belongs.
| FAMILY NAME | FUNCTIONAL GROUP STRUCTURE* | SIMPLE EXAMPLE | NAME ENDING |
| Alkane | Contains only C—H and C—C single bonds | CH_3CH_3 Ethane | -ane |
| Alkene | -ene | ||
| Alkyne | -yne | ||
| Aromatic |  |
 Benzene Benzene |
None |
| Alkyl halide | CH_3 – Cl Methyl chloride | None | |
| Alcohol | CH_3 – OH Methyl alcohol (Methanol) | -ol | |
| Ether | CH_3 – O – CH_3 Dimethyl ether | None | |
| Amine | CH_3 – NH_2 Methylamine | -amine | |
| Aldehyde |  |
\begin{array}{r c}\underset{||}{O} \qquad \> \\ CH_3-C-H \end{array} Acetaldehyde (Ethanal) | -al |
| Ketone | 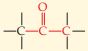 |
\begin{array}{r c}\underset{||}{O} \qquad \quad \> \\ CH_3-C-CH_3 \end{array} Acetone | -one |
| Carboxylic acid |  |
\begin{array}{r c}\underset{||}{O} \qquad \enspace \> \\ CH_3-C-OH \end{array} Acetic acid | -ic acid |
| Anhydride |  |
\begin{array}{r c}\underset{||}{O} \qquad \quad \> \underset{||}{O} \qquad \quad \> \\ CH_3-C-O-C-CH_3 \end{array} Acetic anhydride | None |
| Ester |  |
\begin{array}{r c} \underset{||}{O} \qquad \qquad \quad \> \\ CH_3-C-O-CH_3 \end{array} Methyl acetate | -ate |
| Amide |  |
\begin{array}{r c} \underset{||}{O} \qquad \quad \; \\ CH_3-C-NH_2 \end{array} Acetamide | -amide |
 |
|||
| *The bonds whose connections are not specified are assumed to be attached to carbon or hydrogen atoms in the rest of the molecule. | |||
Learn more on how we answer questions.
(a) This compound contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, so it is a hydrocarbon. There is a carbon-carbon double bond, so it is an alkene.
(b) The O — H group bonded to tetravalent carbon identifies this compound as an alcohol.
(c) This compound also contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, which identifies it as a hydrocarbon. The six-membered carbon ring with alternating double bonds also identifies this compound as an aromatic hydrocarbon compound.
(d) The carbon-oxygen double bond in the middle of the carbon chain (as opposed to at either end of the chain) identifies this compound as a ketone.