Question 27.7: In the panel shown in Fig. P.27.7 the area, As, of the centr......
In the panel shown in Fig. P.27.7 the area, A_{\mathrm{s}}, of the central stringer is to be designed so that the stress in it is 80 percent of the constant stress, \sigma_{e}, in the edge members, each of area B. Assuming that the sheet, which is of constant thickness, t, carries only shear stress and that transverse strains are prevented, derive expressions for A_{\mathrm{s}}, and B in terms of the applied loads and the appropriate elastic moduli, E for the longitudinal members and G for the sheet. Evaluate these expressions in the case where P = 450,000 N; P_{s}=145.000\,\,\mathrm{N}; S =350 N/mm; \sigma_{e}=275\ \mathrm{N/mm^{2}};\,l=1.250\ \mathrm{mm}; b = 250 mm; t = 2.5 mm; and G = 0.38E. Find the fraction of the total tension at the abutment carried by the stringer.

Learn more on how do we answer questions.
Initially directions for the shear flows, q, are chosen as shown in Fig. S.27.7(a). The panel is symmetrical about its horizontal centre line so that only half need be considered.
For equilibrium of the element of the top boom shown in Fig. S.27.7(b),
i.e.,
{\frac{\partial P_{\mathrm{B}}}{\partial z}}=S-q (i)
Also, for equilibrium of the element of the central stringer shown in Fig. 27.7(c),
P_{\mathrm{{A}}}+{\frac{\partial P_{\mathrm{{A}}}}{\partial z}}\delta z-P_{\mathrm{{A}}}-2q\delta z=0i.e.,
{\frac{\partial P_{\mathrm{A}}}{\partial z}}=2q (ii)
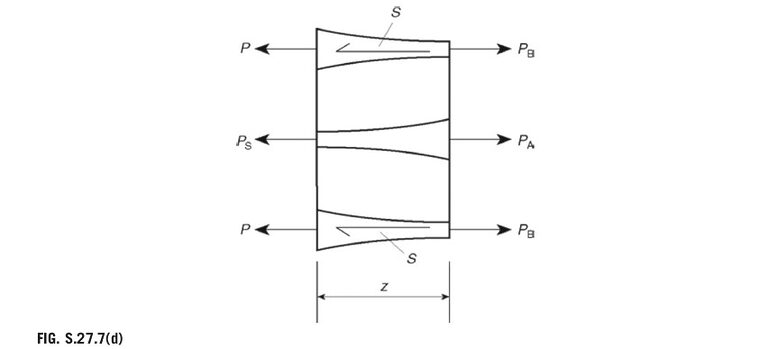
For equilibrium of the length, z, of the panel shown in Fig. S.27.7(d),
2P_{\mathrm{B}}+P_{\mathrm{A}}-2S z-2P-P_{S}=0i.e.,
P_{\mathrm{A}}=2P+P_{\mathrm{S}}+2S z-2P_{\mathrm{B}} (iii)
The compatibility of displacement condition for the top boom and central stringer is shown in Fig. S.27.7(e). Thus,
(1+\varepsilon_{\mathrm{A}})\delta z=(1+\varepsilon_{\mathrm{B}})\delta z+b{\frac{\partial\gamma}{\mathrm{d}z}}\delta zi.e.,
{\frac{\mathrm{d}\gamma}{\mathrm{d}z}}={\frac{1}{b}}(\varepsilon_{\mathrm{A}}-\varepsilon_{\mathrm{B}}) (iv)
Now
\varepsilon_{\mathrm{A}}={\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{A}}}{E}}\ \ {\mathrm{and}}\ \ \varepsilon_{\mathrm{B}}={\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{B}}}{E}}={\frac{\sigma_{e}}{E}}={\mathrm{constant}}Also \sigma_{\mathrm{A}}=0.8\sigma_{\mathrm{e}} so that Eq. (iv) becomes
{\frac{\mathrm{d}\gamma}{\mathrm{d}z}}=-{\frac{0.2\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}{b E}} (v)
In Eq. (v) \gamma=q/G t, hence
{\frac{\mathrm{d}q}{\mathrm{d}z}}=-{\frac{0.2G t}{b E}}\sigma_{\mathrm{e}} (vi)
Substituting for q in Eq. (vi) from (i) gives
{\frac{\partial^{2}P_{\mathrm{B}}}{\partial z^{2}}}={\frac{0.2G t}{b E}}\sigma_{\mathrm{c}}so that
P_{\mathrm{B}}={\frac{0.1G t e_{\mathrm{c}}}{b E}}z^{2}+C z+D (vii)
When z=0,P_{\mathrm{B}}=P so that, from Eq. (vii), D=P. Also, when z=l, q = 0 so that, from Eq. (i),
∂PB/∂z = S at z=l. Hence, from Eq. (vii),
and
P_{\mathrm{B}}={\frac{0.1G t\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}{b E}}z^{2}+\left(S-{\frac{0.2G t\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}l}{b E}}\right)z+P (viii)
Now P_{\mathrm{{B}}}=\sigma_{\mathrm{{e}}}B so that, from Eq. (viii),
B=\frac{0.1G t}{b E}z^{2}+\frac{1}{\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}\biggl[\biggl(S-\frac{0.2G t\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}{ l}}{b E}\biggr)z+P\biggr] (ix)
Substituting for P_{\mathrm{{B}}} from Eq. (viii) in (iii) gives
P_{\mathrm{A}}={\frac{0.4G t\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}{b E}}\left(l z-{\frac{z^{2}}{2}}\right)+P_{S} (x)
But P_{\mathrm{A}}=A_{\mathrm{S}}0.8\sigma_{\mathrm{e}} so that, from Eq. (x),
A_{S}={\frac{G t}{2b E}}\left({l z-{\frac{z^{2}}{2}}}\right)+{\frac{1.25P_{S}}{\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}} (xi)
Substituting the given values in Eqs (ix) and (xi) gives
B=3.8\times10^{-4}z^{2}+0.3227z+1636.4 (xii)
and
A_{S}=2.375z-9.5\times10^{-4}z^{2}+659.1 (xiii)
From Eq. (xiii), when z=1250 mm, A_{S}=2143.5\ \mathrm{mm}^{2}. Then
P_{\mathrm{A}}=0.8\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}A_{\mathrm{S}}=0.8\times275\times2143.5=471\,570\mathrm{N}The total load, P_{\mathrm{T}}, carried by the panel at the built-in end is
P_{\mathrm{T}}=2\times450\,000+145\,0000+2\times350\times1250=1\,920\,000\,\mathrm{N}Therefore, the fraction of the load carried by the stringer is 471 570/1 920 000 = 0.25.