Question 1.SGPYQ.6: Two AC sources feed a common variable resistive load as show......
Two AC sources feed a common variable resistive load as shown in the figure given below. Under the maximum power transfer condition, the power absorbed by the load resistance R_{ L } is
(a) 2200 W (b) 1250 W
(c) 1000 W (d) 625 W

Learn more on how do we answer questions.
For maximum power transfer,
R_{ L }=\left|Z_{ Th }\right| \quad \text { and } \quad P=I^2 R_{ L }
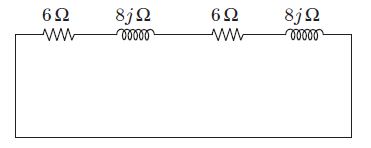
To find the Thevenin impedance, short circuit the voltage source
\begin{aligned} Z_{ Th } & =(6+8 j \Omega)||(6+8 j \Omega) \\ & =\frac{(6+8 j \Omega) \times(6+8 j \Omega)}{(6+8 j \Omega)+(6+8 j \Omega)} \\ & =3+4 j \Omega \end{aligned}
Therefore, R_{ L }=\sqrt{3^2+4^2}=\sqrt{9+16}=\sqrt{25}=5 \Omega
To find the Thevenin’s voltage, open the load:
By nodal analysis method,
\begin{gathered} \frac{V_{ Th }-110 \angle 0^{\circ}}{6+8 j}+\frac{V_{ Th }-90 \angle 0^{\circ}}{6+8 j}=0 \\ V_{ Th }-100 \angle 0^{\circ} V \end{gathered}
Therefore,
\begin{aligned} P & =\frac{V_{ Th }}{R_{ Th }+R_{ L }} \cdot R_{ L }=\left|\frac{100}{(3+4 j)+5}\right|^2 \times 5 \\ & =\frac{(100)^2 \times 5}{80}=625 W \end{aligned}