Question 3.11: A heatsink model of a central processing unit (CPU) is shown...
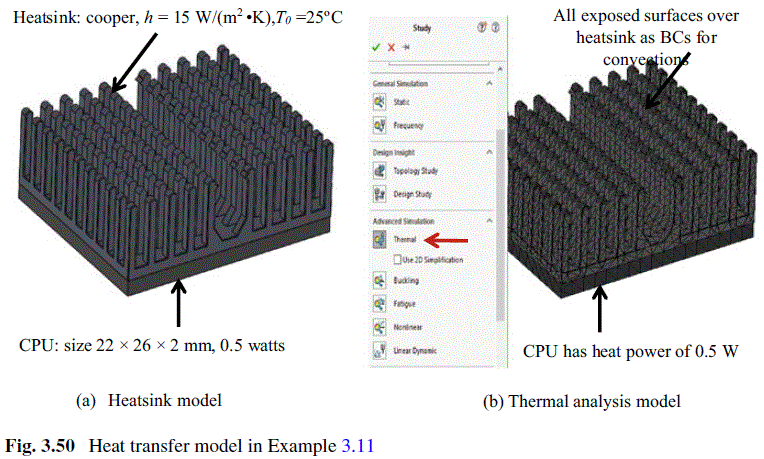
A heatsink model of a central processing unit (CPU) is shown in Fig. 3.50. Assume that the heatsink uses copper materials, the heat transfer coefficient under the forced air is h = 15 W/(m²·K), and the ambient temperature of the operating environment is given as T_{0} = 25 °C. Find (1) the maximum temperature in CPU and (2) the maximum heat power the heatsink can dissipate when the maximum temperature can be below T_{max} = 60 °C.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
The heat transfer model for the heatsink has been defined in Fig. 3.50b. Two boundary conditions are (1) the convection condition on all of the exposed surfaces of heatsink, and (2) the heat power defined in the body of CPU. The materials of CPU is set as silicon. The mesh is created using the default settings. Running the simulation yields the results of Fig. 3.51a, b for the distributions of the temperature and temperature gradients, respectively. It has been found the maximum temperature at the center of CPU is T_{max} = 30.95 °C.
The above thermal analysis model is used to create a design study as shown in Fig. 3.52. The heat power (P) from CPU is set as the simulation variable, and the analysis range is set as P ∈ [0.5, 3] with a step of 0.25 (W). The result of the design study in Fig. 3.53 shows that the heatsink reach its maximum temperature T_{max} = 57.71 °C < 60 °C when the heat power of CPU P = 2.75 (W).


