Question 6.15: Calculate the transmission coefficient Ƭ for a wave that is...
Calculate the transmission coefficient \mathcal {T } for a wave that is propagating in the +z direction in a coaxial cable. The relative dielectric constant of the separating dielectric in the region z < 0 is 2 and in the region z > 0 is 3. The physical dimensions of the cable are the same in all regions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Using (6.65) and the results given in Table 6-2, we write
\mathcal {T }=\frac{V_{L}}{V_{1}}=\frac{2 Z_{L}}{Z_{L}+Z_{C}} (6.65)
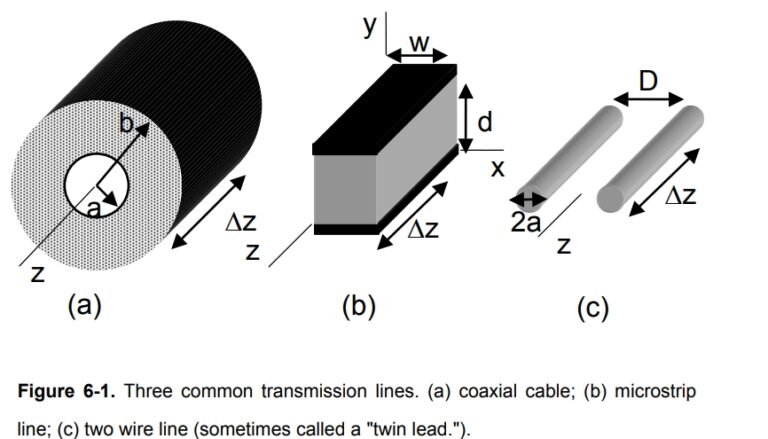
| Velocity of propagation | Characteristic impedance | |
| coaxial cable | v=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\hat{L} \hat{C}}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu \varepsilon}} | Z_{c}=\sqrt{\frac{\hat{L}}{\hat{C}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mu}{\varepsilon}}\left(\frac{\ln \left(\frac{b}{a}\right)}{2 \pi}\right) |
| microstrip line | v=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\hat{L} \hat{C}}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu \varepsilon}} | Z_{c}=\sqrt{\frac{\hat{L}}{\hat{C}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mu}{\varepsilon}}\left(\frac{d}{w}\right) |
| twin lead | v=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\hat{L} \hat{C}}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu \varepsilon}} | Z_{c}=\sqrt{\frac{\hat{L}}{\hat{C}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mu}{\varepsilon}}\left(\frac{\cosh ^{-1}\left(\frac{D}{2 a }\right)}{\pi}\right) |
| Table 6-2. The velocity of propagation and the characteristic impedance of the various transmission lines shown in Figure 6-1. The parameters for the material between the two conductors are the permeability µ = µrµo and the permittivity ε = εrεo. | ||
\mathcal {T }=\frac{2 \sqrt{\frac{\mu}{3 \varepsilon_{0}}}\left(\frac{\ln \left(\frac{b}{a}\right)}{2 \pi}\right)}{\sqrt{\frac{\mu}{3 \varepsilon_{0}}}\left(\frac{\ln \left(\frac{b}{a}\right)}{2 \pi}\right)+\sqrt{\frac{\mu}{2 \varepsilon_{0}}}\left(\frac{\ln \left(\frac{b}{a}\right)}{2 \pi}\right)}=\frac{\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}}{\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}=0.9