Question 22.2: Enzyme Classification Using Table 22.1, identify the chemica...
Enzyme Classification
Using Table 22.1, identify the chemical reaction catalyzed by each of the following:
(a) Alcohol dehydrogenase
(b) Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase
| Table 22.1 Classification of Enzymes | |||
| Section Number in This Book |
Reaction Catalyzed | Typical Example | Class |
| 27.2 | \underset{\text{L-(+)-Lactate}\hspace{65 pt}\text{Pyruvate}}{\begin{matrix} \text{CH}_{3}-\underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}-\text{COO}^{-} \longrightarrow \text{CH}_{3}-\underset{||}{\text{C}}-\text{COO}^{-} \\ \hspace{-10 pt}\text{OH}\hspace{93 pt}\text{O} \end{matrix} } | Lactate dehydrogenase | 1. Oxidoreductases |
| 27.8 | \underset{\substack{\text{Aspartate}}}{\begin{matrix}\hspace{-23 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-}\\ \hspace{-32 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}-{\text{NH}_{3}}^{+}\\ \hspace{-23 pt} \text{COO}^{-}\\ \text{}\end{matrix} } + \underset{\substack{\text{α-Ketoglutarate}}}{\begin{matrix} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-}\\ \underset{|}{\text{C}}=\text{O}\\ \hspace{-10 pt } \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \hspace{-10 pt } \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \text{COO}^{-}\end{matrix} }\longrightarrow\underset{\substack{\text{Oxaloacetate}}}{\begin{matrix} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-}\\ \hspace{-10 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \underset{|}{\text{C}}=\text{O}\\ \text{COO}^{-}\\ \text{}\end{matrix} } + \underset{\substack{\text{Glutamate}}}{\begin{matrix} \hspace{-23 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-}\\ \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}-{\text{NH}_{3}}^{+}\\ \hspace{-32 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \hspace{-32 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2}\\ \hspace{-23 pt} \text{COO}^{-}\end{matrix} } | Aspartate amino transferase or aspartate transaminase | 2. Transferases |
| 23.3 | \begin{matrix} \text{CH}_{3}-\underset{||}{\text{C}}-\text{OCH}_{2}\text{CH}_{2}\overset{+}{\text{N}}{(\text{CH}_{3})_{3}} + \text{H}_{2}\text{O} \longrightarrow \text{CH}_{3}\text{COOH} + \text{HOCH}_{2}\text{CH}_{2}\overset{+}{\text{N}}{(\text{CH}_{3})_{3}} \\ \hspace{-4 pt} \text{O} \hspace{160 pt} \substack{\text{Acetic acid}} \hspace{47 pt}\substack{\text{Choline}} \\ \hspace{ -200 pt} \substack{\text{Acetylcholine}} \end{matrix} | Acetylcholinesterase | 3. Hydrolases |
| 26.4 | \begin{matrix} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-}\hspace{99 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{OO}^{-} \\ \hspace{-11 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2} \hspace{108 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}_{2} \\ \hspace{25 pt} \underset{||}{\text{C}}-\text{COO}^{-}+\text{H}_{2}\text{O} \longrightarrow \hspace{24 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H}-\text{COO}^{-} \\ \hspace{-5 pt} \underset{|}{\text{C}}\text{H} \hspace{85 pt} \text{HO}-\underset{|}{\text{C}}-\text{H} \\ \text{COO}^{-} \hspace{98 pt} \text{COO}^{-}\\ \substack{cis-\text{Aconitate}\hspace{75 pt}\text{Isocitrate}} \end{matrix} | Aconitase | 4. Lyases |
| 27.2 | 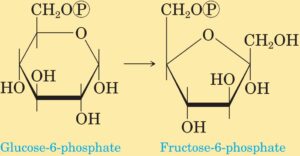 |
Phosphohexose isomerase | 5. Isomerases |
| 25.6 | \text{ATP} + \text{L-tyrosine} + \text{tRNA} \longrightarrow \text{L-tyrosyl-tRNA} + \text{AMP} + \text{PP}_{\text{i}} | Tyrosine-tRNA synthetase | 6. Ligases |
Strategy
With most enzymes, the name alone gives a good indication of what it does. Usually, as in these two examples, the name of the enzyme includes the molecule being acted on plus the action being done.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
(a) Alcohol dehydrogenase would take an alcohol and remove hydrogen, creating a carbonyl group where there once was a hydroxyl. In this case it primarily uses ethanol and creates acetaldehyde. However, alcohol dehydrogenase can also perform the same action, to a lesser degree, on methanol.
(b) An isomerase converts one molecule into another molecule with the same empirical formula, such as \text{C}_{\text{x}}\text{H}_{\text{y}}\text{O}_{\text{z}}. Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase converts the phosphorylated sugar ribose (an aldose) to ribulose-5-phosphate (a ketose).
■ Quick Check 22.2
In Chapter 20 we saw the action of the enzyme lipase. What does lipase do and how would it be classified?