A pipe with an outside diameter of 140 mm and a wall thickness of 7 mm is subjected to the 16-kN load shown in Figure P15.79. The internal pressure in the pipe is 2.50 MPa, and the yield strength of the steel is \sigma_{Y} = 240 MPa.
(a) Determine the factors of safety predicted at points H and K by the maximum-shear-stress theory of failure.
(b) Determine the Mises equivalent stresses at points H and K.
(c) Determine the factors of safety at points H and K predicted by the maximum-distortion-energy theory.
Question 15.79: A pipe with an outside diameter of 140 mm and a wall thickne...

The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Section properties:
\begin{aligned}&d=140 mm -2(7 mm )=126 mm \\&A=\frac{\pi}{4}\left[(140 mm )^{2}-(126 mm )^{2}\right]=2,924.823 mm ^{2} \\&J=\frac{\pi}{32}\left[(140 mm )^{4}-(126 mm )^{4}\right]=12.970 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4} \\&I_{y}=I_{z}=\frac{\pi}{64}\left[(140 mm )^{4}-(126 mm )^{4}\right]=6.485 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4} \\&Q=\frac{1}{12}\left[(140 mm )^{3}-(126 mm )^{3}\right]=61,968.667 mm ^{3}\end{aligned}
Vector expression for the 16-kN load:
The 16-kN load can be expressed in vector form as:
The equivalent forces acting at H and K are thus
\begin{aligned}&F_{x}=0 N \\&F_{y}=-13,106.433 N \\&F_{z}=9,177.223 N\end{aligned}The position vector from the section of interest to a point on the line of action of F is:
r =(0.7 m ) i +(1.3 m ) kThe equivalent moments are found from the cross-product r × F.
\begin{aligned}r \times F &=\left|\begin{array}{ccc} i & j & k \\0.7 & 0 & 1.3 \\0 & -13,106.433 & 9,177.223\end{array}\right| \\&=17,038.363 N – m i -6,424.056 N – m j -9,174.503 N – m k\end{aligned}
Equivalent moments:
\begin{aligned}M_{x} &=17.0384 \times 10^{6} N – mm \\M_{y} &=-6.4241 \times 10^{6} N – mm \\M_{z} &=-9.1745 \times 10^{6} N – mm\end{aligned}Each of the non-zero forces and moments will be evaluated to determine whether stresses are created at the point of interest.
(a) Consider point H.
Force F_{y} does not cause either a normal stress or a shear stress at H.
Force F_{z} creates a transverse shear stress in the xz plane at H. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x z}=\frac{(9,177.223 N )\left(61,968.667 mm ^{3}\right)}{\left(6.485 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4}\right)[(140 mm )-(126 mm )]}=6.264 MPaMoment M _{x}, which is a torque, creates a torsion shear stress in the xz plane at H. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x z}=\frac{M_{x} c}{J}=\frac{\left(17.0384 \times 10^{6} N – mm \right)(140 mm / 2)}{12.970 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4}}=91.956 MPaMoment M _{y} does not create bending stress at H because H is located on the neutral axis for bending about the y axis.
Moment M _{z} creates bending stress at H. The magnitude of this stress is:
\sigma_{x}=\frac{M_{z} y}{I_{z}}=\frac{\left(9.1745 \times 10^{6} N – mm \right)(140 mm / 2)}{6.485 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4}}=99.031 MPaStresses due to internal pressure:
The 2.50-MPa internal fluid pressure creates tension normal stresses in the 7-mm-thick wall of the pipe.
The longitudinal stress (which acts in the x direction) in the pipe wall is:
and the circumferential stress is:
\sigma_{\text {hoop }}=\frac{p d}{2 t}=\frac{(2.50 MPa )(126 mm )}{2(7 mm )}=22.50 MPa ( T )The hoop stress acts in the z direction at H and in the y direction at K.
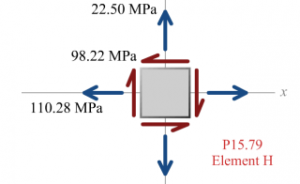
Summary of stresses at H:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{x} &=99.030 MPa +11.25 MPa =110.280 MPa ( T ) \\\sigma_{z} &=22.50 MPa ( T ) \\\tau_{x z} &=6.264 MPa +91.956 MPa =98.220 MPa\end{aligned}Principal stress calculations for point H:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{p 1, p 2} &=\frac{(110.280 MPa )+(22.50 MPa )}{2} \pm \sqrt{\left(\frac{(110.280 MPa )-(22.50 MPa )}{2}\right)^{2}+(-98.220 MPa )^{2}} \\&=66.390 MPa \pm 107.580 MPa\end{aligned}therefore, \sigma_{p 1}=173.970 MPa and \sigma_{p 2}=-41.190 MPa
Consider point K.
Force F _{y} creates a transverse shear stress in the xy plane at K. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
Force F _{z} does not cause either a normal stress or a shear stress at K.
Moment M _{x}, which is a torque, creates a torsion shear stress in the xy plane at K. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x y}=\frac{M_{x} c}{J}=\frac{\left(17.0384 \times 10^{6} N – mm \right)(140 mm / 2)}{12.970 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4}}=91.956 MPaMoment M _{y} creates bending stress at K. The magnitude of this stress is:
\sigma_{x}=\frac{M_{y} z}{I_{y}}=\frac{\left(6.4241 \times 10^{6} N – mm \right)(140 mm / 2)}{6.485 \times 10^{6} mm ^{4}}=69.341 MPaMoment M _{z} does not create bending stress at K because K is located on the neutral axis for bending about the z axis.

Summary of stresses at K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{x} &=-69.341 MPa +11.25 MPa =58.091 MPa ( C ) \\\sigma_{y} &=22.50 MPa ( T ) \\\tau_{x y} &=-8.946 MPa -91.956 MPa =-100.902 MPa\end{aligned}Principal stress calculations for point K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{p 1, p 2} &=\frac{(-58.091 MPa )+(22.50 MPa )}{2} \pm \sqrt{\left(\frac{(-58.091 MPa )-(22.50 MPa )}{2}\right)^{2}+(-100.902 MPa )^{2}} \\&=-17.796 MPa \pm 108.651 MPa\end{aligned}therefore, \sigma_{p 1}=90.855 MPa and \sigma_{p 2}=-126.446 MPa
(a) Maximum-Shear-Stress Theory
Element H:
The factor of safety associated with this state of stress is:
FS _{H}=\frac{240 MPa }{215.160 MPa }=1.115Element K:
\left|\sigma_{p 1}-\sigma_{p 2}\right|=|90.855 MPa -(-126.446 MPa )|=217.301 MPaThe factor of safety associated with this state of stress is:
FS _{K}=\frac{240 MPa }{217.301 MPa }=1.104
(b) Mises equivalent stresses at points H and K:
Element H:
Element K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{M, K} &=\left[\sigma_{p 1}^{2}-\sigma_{p 1} \sigma_{p 2}+\sigma_{p 2}^{2}\right]^{1 / 2} \\&=\left[(90.855 MPa )^{2}-(90.855 MPa )(-126.446 MPa )+(-126.446 MPa )^{2}\right]^{1 / 2} \\&=189.028 MPa =189.0 MPa\end{aligned}
(c) Maximum-Distortion-Energy Theory:
Element H:
Element K:
FS _{K}=\frac{240 MPa }{189.028 MPa }=1.270
Related Answered Questions
Section properties:
A=\frac{\pi}{4}(1.5 in...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...
Section properties:
J=\frac{\pi}{32}(50 mm...
Principal stresses:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{...
Principal stresses:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{...
The torque in the driveshaft is:
T=\frac{P}...
The torque in the driveshaft is:
T=\frac{P}...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...