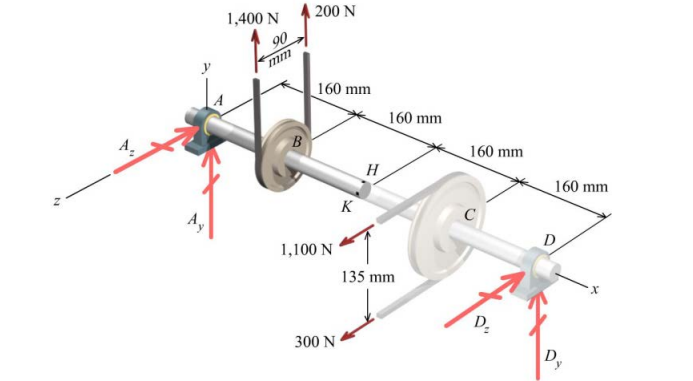
A steel shaft with an outside diameter of 20 mm is supported in flexible bearings at its ends. Two pulleys are keyed to the shaft, and the pulleys carry belt tensions as shown in Figure P15.78. The yield strength of the steel is \sigma_{Y} = 350 MPa.
(a) Determine the factors of safety predicted at points H and K by the maximum-shear-stress theory of failure.
(b) Determine the Mises equivalent stresses at points H and K.
(c) Determine the factors of safety at points H and K predicted by the maximum-distortion-energy theory.
Question 15.78: A steel shaft with an outside diameter of 20 mm is supported...

The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\frac{\pi}{4}(20 mm )^{2}=314.159 mm ^{2} & J=\frac{\pi}{32}(20 mm )^{4}=15,707.963 mm ^{4} \\Q=\frac{(20 mm )^{3}}{12}=666.667 mm ^{3} & I_{y}=I_{z}=\frac{\pi}{64}(20 mm )^{4}=7,853.982 mm ^{4}\end{array}

__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Equilibrium of entire shaft:
\begin{aligned}&\Sigma F_{y}=A_{y}+D_{y}+1,400 N +200 N =0 \\&\Sigma F_{z}=-A_{z}-D_{z}+1,100 N +300 N =0 \\&\Sigma M_{A, y \text { axis }}=-(1,100 N )(480 mm )-(300 N )(480 mm )+(640 mm ) D_{z}=0 \\&\Sigma M_{A, z \text { axis }}=(1,400 N )(160 mm )+(200 N )(160 mm )+(640 mm ) D_{y}=0\end{aligned}therefore
D_{y}=-400 N , A_{y}=-1,200 N , D_{z}=1,050 N , \text { and } A_{z}=350 N__________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Detail of equivalent forces at H and K: Detail of equivalent moments at H and K:


\begin{aligned}F_{x} &=0 N \\F_{y} &=-400 N \\F_{z} &=1,100 N +300 N -1,050 N \\&=350 N\end{aligned} \begin{gathered}M_{x}=(1,100 N )(135 mm / 2)-(300 N )(135 mm / 2) \\=54,000 N – mm \\M_{y}=(1,050 N )(320 mm )-(1,100 N )(160 mm ) \\\quad-(300 N )(160 mm )=112,000 N – mm \\M_{z}=-(400 N )(320 mm )=-128,000 N – mm\end{gathered}
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Each of the non-zero forces and moments will be evaluated to determine whether stresses are created at the point of interest.
Consider point H.
Force F _{ y } does not cause either a normal stress or a shear stress at H.
Force F _{ z } creates a transverse shear stress in the xz plane at H. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x z}=\frac{(350 N )\left(666.667 mm ^{3}\right)}{\left(7,853.982 mm ^{4}\right)(20 mm )}=1.485 MPaMoment M _{x}, which is a torque, creates a torsion shear stress in the xz plane at H. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x z}=\frac{M_{x} c}{J}=\frac{(54,000 N – mm )(20 mm / 2)}{15,707.963 mm ^{4}}=34.377 MPaMoment M _{y} does not create bending stress at H because H is located on the neutral axis for bending about the y axis.
Moment M _{z} creates bending stress at H. The magnitude of this stress is:
\sigma_{x}=\frac{M_{z} y}{I_{z}}=\frac{(128,000 N – mm )(20 mm / 2)}{7,853.982 mm ^{4}}=162.975 MPa

Summary of stresses at H:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{x} &=162.975 MPa \\\sigma_{z} &=0 MPa \\\tau_{x z} &=1.485 MPa +34.377 MPa =35.863 MPa\end{aligned}Principal stress calculations for point H:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{p 1, p 2} &=\frac{(162.975 MPa )+(0 MPa )}{2} \pm \sqrt{\left(\frac{(162.975 MPa )-(0 MPa )}{2}\right)^{2}+(-35.863 MPa )^{2}} \\&=81.487 MPa \pm 89.030 MPa\end{aligned}therefore, \sigma_{p 1}=170.517 MPa and \sigma_{p 2}=-7.543 MPa
Consider point K.
Force F _{y} creates a transverse shear stress in the xy plane at K. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
Force F _{z} does not cause either a normal stress or a shear stress at K.
Moment M _{x}, which is a torque, creates a torsion shear stress in the xy plane at K. The magnitude of this shear stress is:
\tau_{x y}=\frac{M_{x} c}{J}=\frac{(54,000 N – mm )(20 mm / 2)}{15,707.963 mm ^{4}}=34.377 MPaMoment M _{y} creates bending stress at K. The magnitude of this stress is:
\sigma_{x}=\frac{M_{y} z}{I_{y}}=\frac{(112,000 N – mm )(20 mm / 2)}{7,853.982 mm ^{4}}=142.603 MPaMoment M _{z} does not create bending stress at K because K is located on the neutral axis for bending about the z axis.

Summary of stresses at K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{x} &=142.603 MPa \\\sigma_{y} &=0 MPa \\\tau_{x y} &=-1.698 MPa -34.377 MPa =-36.075 MPa\end{aligned}Principal stress calculations for point K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{p 1, p 2} &=\frac{(142.603 MPa )+(0 MPa )}{2} \pm \sqrt{\left(\frac{(142.603 MPa )-(0 MPa )}{2}\right)^{2}+(-36.075 MPa )^{2}} \\&=71.301 MPa \pm 79.908 MPa\end{aligned}therefore, \sigma_{p 1}=151.210 MPa and \sigma_{p 2}=-8.607 MPa
(a) Maximum-Shear-Stress Theory
Element H:
The factor of safety associated with this state of stress is:
FS _{H}=\frac{350 MPa }{178.060 MPa }=1.966Element K:
\left|\sigma_{p 1}-\sigma_{p 2}\right|=|151.210 MPa -(-8.607 MPa )|=159.816 MPaThe factor of safety associated with this state of stress is:
FS _{K}=\frac{350 MPa }{159.816 MPa }=2.19
(b) Mises equivalent stresses at points H and K:
Element H:
Element K:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{M, K} &=\left[\sigma_{p 1}^{2}-\sigma_{p 1} \sigma_{p 2}+\sigma_{p 2}^{2}\right]^{1 / 2} \\&=\left[(151.210 MPa )^{2}-(151.210 MPa )(-8.607 MPa )+(-8.607 MPa )^{2}\right]^{1 / 2} \\&=155.691 MPa =155.7 MPa\end{aligned}
(c) Maximum-Distortion-Energy Theory:
Element H:
Element K:
FS _{K}=\frac{350 MPa }{155.691 MPa }=2.25
Related Answered Questions
Section properties:
A=\frac{\pi}{4}(1.5 in...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...
Section properties:
J=\frac{\pi}{32}(50 mm...
Principal stresses:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{...
Principal stresses:
\begin{aligned}\sigma_{...
The torque in the driveshaft is:
T=\frac{P}...
The torque in the driveshaft is:
T=\frac{P}...
Section properties:
\begin{aligned}&d=1...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...
Section properties:
\begin{array}{ll}A=\fra...