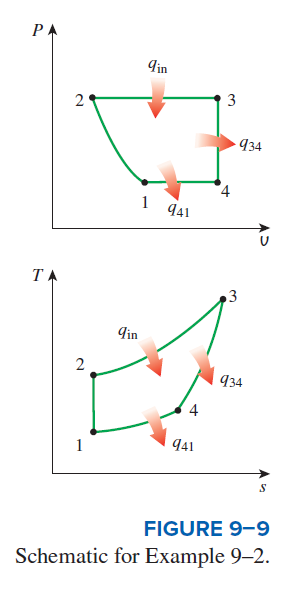
The four processes of an air-standard cycle are described. The cycle is to be shown on P-v and T-s diagrams, and the maximum temperature in the cycle and the thermal efficiency are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 The air-standard assumptions are applicable. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. 3 Air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats.
Properties The properties of air at room temperature are c_{p}=1.005 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K}, c_{v}=0.718 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K}, and k=1.4 (Table A-2a).
Analysis (a) The cycle is shown on P-v and T-s diagrams in Fig. 9-9 .
(b) From the ideal gas isentropic relations and energy balance,
\begin{aligned}T_{2}&=T_{1}\left(\frac{P_{2}}{P_{1}}\right)^{(k-1) / k}=(300 \mathrm{~K})\left(\frac{1000 \mathrm{kPa}}{100 \mathrm{kPa}}\right)^{0.4 / 1.4}=579.2 \mathrm{~K} \\\\q_{\mathrm{in}}&=h_{3}-h_{2}=c_{p}\left(T_{3}-T_{1}\right) \\\\2800 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg}&=(1.005 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K})\left(T_{3}-579.2\right) \longrightarrow T_{\max }=T_{3}=3360 \mathrm{~K}\end{aligned}
(c) The temperature at state 4 is determined from the ideal gas relation for a fixed mass,
\frac{P_{3} v_{3}}{T_{3}}=\frac{P_{4} v_{4}}{T_{4}} \longrightarrow T_{4}=\frac{P_{4}}{P_{3}} T_{3}=\frac{100 \mathrm{kPa}}{1000 \mathrm{kPa}}(3360 \mathrm{~K})=336 \mathrm{~K}
The total amount of heat rejected from the cycle is
\begin{aligned}q_{\mathrm{out}} &=q_{34, \mathrm{out}}+q_{41, \mathrm{out}}=\left(u_{3}-u_{4}\right)+\left(h_{4}+h_{1}\right) \\&=c_{v}\left(T_{3}-T_{4}\right)+c_{p}\left(T_{4}-T_{1}\right) \\&=(0.718 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K})(3360-336) \mathrm{K}+(1.005 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K})(336-300) \mathrm{K} \\&=2212 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg}\end{aligned}
Then, the thermal efficiency is determined from its definition to be
\eta_{\text {th }}=1-\frac{q_{\text {out }}}{q_{\text {in }}}=1-\frac{2212 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg}}{2800 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kg}}=0.210 \text { or } 21.0 \%
Discussion The assumption of constant specific heats at room temperature is not realistic in this case since the temperature changes involved are too large.