Calculation of the Fugacity of a Species in a Mixture by Two Methods
Compute the fugacity of both carbon dioxide and methane in an equimolar mixture at 500 K and 500 bar using (a) the Lewis-Randall rule and (b) the Peng-Robinson equation of state.
Calculation of the Fugacity of a Species in a Mixture by Two Methods
Compute the fugacity of both carbon dioxide and methane in an equimolar mixture at 500 K and 500 bar using (a) the Lewis-Randall rule and (b) the Peng-Robinson equation of state.
a. The Lewis-Randall rule is
\bar{f}_{ i }(T, P, \underline{y})=y_{ i } f_{ i }(T, P)=y_{ i }\left(\frac{f}{P}\right)_{ i } P
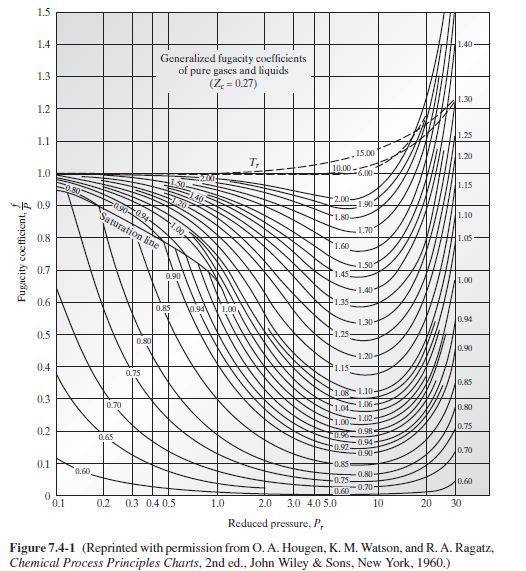
From Fig. 7.4-1, we have
| T_{r} | P_{r} | f / P | |
| CO _{2} | 1.644 | 6.78 | ∼ 0.77 |
| CH _{4} | 2.623 | 10.87 | ∼ 1.01* |
| *Since it is very difficult to read the fugacity coefficient curve in the range of the reduced temperature and pressure for methane in this problem, this entry was obtained from the tables inO.A.Hougen, K. M.Watson, and R.A. Ragatz, Chemical Process Principles, Part II, Thermodynamics, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York (1959). | |||
Thus
\bar{f}_{ CO _{2}}=0.5 \times 0.77 \times 500 bar =192.5 bar
and
\bar{f}_{ CH _{4}}=0.5 \times 1.01 \times 500 bar =252.5 bar
b. Using the Peng-Robinson equation of state (Eqs. 6.4-2 and 9.4-8 through 9.4-10) and Aspen Plus^R or the computer programs discussed in Appendix B, we find, for k_{12}=0.0,
P=\frac{R T}{\underline{V}-b}-\frac{a(T)}{\underline{V}(\underline{V}+b)+b(\underline{V}-b)} (6.4-2)
\begin{aligned}a_{\operatorname{mix}} &=\sum_{ i =1}^{ C } \sum_{j=1}^{ C } y_{ i } y_{ j } a_{ ij } \\b_{\operatorname{mix}} &=\sum_{ i =1} y_{ i } b_{ i }\end{aligned} (9.4-8)
a_{ ij }=\sqrt{a_{ ii } a_{ jj }}\left(1-k_{ ij }\right)=a_{ ji } (9.4-9)
\begin{array}{l}\ln \frac{\bar{f}_{ i }^{ V }(T, P, \underline{y})}{y_{ i } P} \\\quad=\ln \bar{\phi}_{ i }^{ V }(T, P, \underline{y}) \\\quad=\frac{b_{ i }}{b_{ mix }}\left(Z_{ mix }^{ V }-1\right)-\ln \left(Z_{ mix }^{ V }-\frac{b_{ mix } P}{R T}\right)\\\quad-\frac{a_{ mix }}{2 \sqrt{2} b_{\text {mix }} R T}\left[\frac{2 \sum_{ j } y_{ j } a_{ ij }}{a_{ mix }}-\frac{b_{ i }}{b_{ mix }}\right] \ln \left[\frac{Z_{ mix }^{ V }+(1+\sqrt{2}) \frac{b_{ mix } P}{R T}}{Z^{ V }+(1-\sqrt{2}) \frac{b_{ mix } P}{R T}}\right]\\\quad =\frac{B_{ i }}{B_{ mix }}\left(Z_{ mix }^{ V }-1\right)-\ln \left(Z_{ mix }^{ V }-B_{ mix }\right)\\\quad -\frac{A_{ mix }}{2 \sqrt{2} B_{ mix }}\left[\frac{2 \sum_{ j } y_{ j } A_{ ij }}{A_{ mix }}-\frac{B_{ i }}{B_{ mix }}\right] \ln \left[\frac{Z_{ mix }^{ V }+(1+\sqrt{2}) B_{ mix }}{Z_{ mix }^{ V }+(1-\sqrt{2}) B_{ mix }}\right]\end{array} (9.4-10)
\bar{f}_{ CO _{2}}=208.71 bar \quad \text { and } \quad \bar{f}_{ CH _{4}}=264.72 bar
and using k_{12}=0.09 (from Table 9.4-1),
\bar{f}_{ CO _{2}}=212.81 bar \quad \text { and } \quad \bar{f}_{ CH _{4}}=269.35 bar
These last values should be the most accurate.
| Table 9.4-1 Binary Interaction Parameters k_{12} for the Peng-Robinson Equation of State* | ||||||||||||||||||
| C _{2} H _{4} | C _{2} H _{6} | C _{3} H _{6} | C _{3} H _{8} | i- C _{4} H _{10} | n- C _{4} H _{10} | i- C _{5} H _{12} | n- C _{6} H _{14} | C _{6} H _{6} | c- C _{6} H _{12} | n- C _{7} H _{16} | n- C _{8} H _{18} | n- C _{10} H _{22} | N _{2} | CO | CO _{2} | SO _{2} | H _{2} S | |
| CH _{4} | 0.022 | -0.003 | 0.033 | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.019 | 0.026 | 0.04 | 0.055 | 0.039 | 0.035 | 0.05 | 0.049 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.136 | 0.08 |
| C _{2} H _{4} | 0.01 | 0.092 | 0.031 | 0.014 | 0.025 | 0.086 | -0.022 | 0.056 | ||||||||||
| C _{2} H _{6} | 0.089 | 0.001 | -0.007 | 0.01 | 0.008 | -0.04 | 0.042 | 0.018 | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.026 | 0.13 | 0.086 | |||
| C _{3} H _{6} | 0.007 | -0.014 | 0.09 | 0.026 | 0.093 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||
| C _{3} H _{8} | -0.007 | 0.003 | 0.027 | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0 | 0 | 0.078 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.08 | ||||||
| i- C _{4} H _{10} | 0 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.047 | |||||||||||||
| n- C _{4} H _{10} | 0.017 | -0.006 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.087 | 0.04 | 0.135 | 0.07 | |||||||||
| i- C _{5} H _{12} | 0.06 | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.092 | 0.04 | 0.121 | 0.06 | |||||||||||
| n- C _{5} H _{12} | 0.01 | -0.004 | 0.007 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.125 | 0.063 | ||||||||||
| n- C _{6} H _{14} | 0.013 | -0.008 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||
| C _{6} H _{6} | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.1 | 0.164 | 0.11 | 0.077 | 0.015 | |||||||||||
| c- C _{6} H _{12} | 0.14 | 0.1 | 0.105 | |||||||||||||||
| n- C _{7} H _{16} | 0 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||
| n- C _{8} H _{18} | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||
| n- C _{10} H _{22} | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.114 | 0.033 | ||||||||||||||
| N _{2} | 0.012 | -0.02 | 0.08 | 0.17 | ||||||||||||||
| CO | 0.03 | 0.054 | ||||||||||||||||
| CO _{2} | 0.136 | 0.097 | ||||||||||||||||
| SO _{2} | ||||||||||||||||||
| H _{2} S | ||||||||||||||||||
| *Obtained from data in “Vapor-Liquid Equilibria for Mixtures of Low-Boiling Substances,” by H. Knapp, R. D¨oring, L. Oellrich, U. Pl¨ocker, and J. M. Prausnitz, DECHEMA Chemistry Data Series, Vol. VI, Frankfurt/Main, 1982, and other sources. Blanks indicate no data are available from which the k12 could be evaluated. In such case use estimates from mixtures of similar compounds. | ||||||||||||||||||