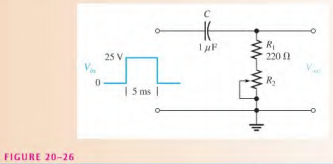
Determine the output voltage waveform for the RC differentiator in Figure 20-26 with the rheostat set so that the total resistance of R_{1} and R_{2} is 2 kΩ.
Question 20.5: Determine the output voltage waveform for the RC differentia...
The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau =R_{tot}C= (2 \ k\Omega )(1 \ \mu F)= 2 \ m sOn the rising edge, the resistor voltage immediately jumps to +25 V. Because the pulse width is 5 ms, the capacitor charges for 2.5 time constants and therefore does not reach full charge. Thus, you must use the formula for a decreasing exponential in order to calculate to what voltage the output decreases by the end of the pulse,
v_{out}=V_{i}e^{-t/RC}= 25e^{-5ms/2ms} = 25 (0.082) = 2.05 \ Vwhere V_{i}= 25 V and t= 5 ms. This calculation gives the resistor voltage ( V_{out} ) at the end of the 5 ms pulse width interval. On the falling edge, the resistor voltage immediately jumps from +2.05 V down to —22.95 V (a 25 V transition). The resulting waveform of the output voltage is shown in Figure 20-27.

Related Answered Questions
Calculate the time constant.
\tau =RC= (2.2...
First, calculate the circuit time constant.
[latex...
The circuit time constant is
\tau = \frac{L...
The inductor charges through the 30 Ω source resis...
First, calculate the time constant,
\tau = ...
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau = ...
f_{h}= \frac{0.35}{t_{r}}= \frac{0.35}{10\t...
(a) The circuit time constant is
\tau =RC= ...
First, calculate the time constant.
\tau =R...
Calculate the time constant.
\tau = \frac{L...