Estimate the power required to compress 5000 kmol/h of HCl at 5 bar, 15°C, to 15 bar.
Question 3.11: Estimate the power required to compress 5000 kmol/h of HCl a...
The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
For HCl, P_{c} = 82 bar, T_{c} = 324.6 K
C^{°}_{p} = 30.30 – 0.72 × 10^{-2} T + 12.5 × 10^{-6} T^{2} – 3.9 × 10^{-9} T^{3} kJ/kmol K
Estimate T_{2} from equations 3.35 and 3.36a
T_{2}=T_{1} \left(\frac{p_{2} }{p_{1} } \right) ^{m} (3.35)
m=\frac{(\gamma-1)}{\gamma E_{p}} (3.36a)
For diatomic gases γ\backsimeq 1.4.
Note: γ could be estimated from the relationship γ = \frac{C_{p} }{C_{v} } = \frac{C_{p} }{C_{p}-R }
At the inlet conditions, the flow rate in 10^{3}/s
= \frac{5000}{3600}\times 22.4\times \frac{288}{273}\times \frac{1}{5}=6.56
From Figure 3.6 E_{p} = 0.73
From equations 3.36a and 3.35
m=\frac{(\gamma-1)}{\gamma E_{p}} (3.36a)
T_{2}=T_{1} \left(\frac{p_{2} }{p_{1} } \right) ^{m} (3.35)
m= \frac{1.4-1}{1.4\times 0.73} =0.39
T_{2}=288\left(\frac{15}{5} \right) ^{0.39} =442 K
T_{ r \left(mean\right) } =\frac{442+228}{2\times 324.6}=1.03
P_{ r \left(mean\right) } =\frac{5+15}{2\times 82}=0.12
AtT_{\left(mean\right) }C^{°}_{p} = 29.14 kJ/kmol K
Correction for pressure from Figure 3.2, 2 kJ/kmol K
C_{p} =29.14 + 2 \simeq 31 kJ/kmol K
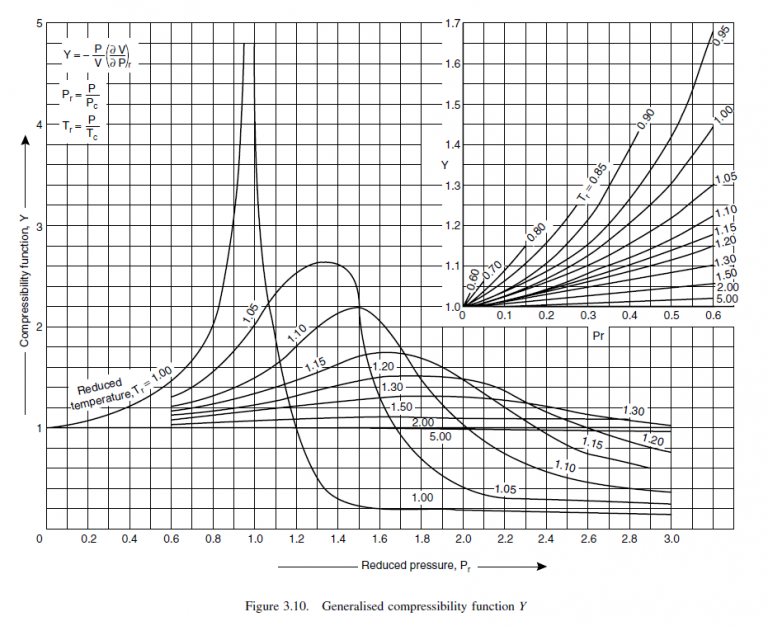
From Figures 3.8, 3.9 and 3.10 at mean conditions:
X = 0.18, Y = 1.04, Z = 0.97
Z at inlet conditions = 0.98
From equations 3.36 and 3.38
m=\frac{ZR}{C_{p} }\left(\frac{1}{E_{p} } +X\right) (3.36)
n\frac{1}{Y-m\left(1+X\right) } (3.38)
m=\frac{0.97×8.314}{31}\left(\frac{1}{0.73 } +0.18\right) = \underline{\underline{0.40} }
n=\frac{1}{1.04 – 0.4\left(1+0.18\right) }=\underline{\underline{1.76} }
From equation 3.31
W polytropic = 0.98 × 288 × 8.314 × \frac{1.76}{1.76 – 1} \left(\left(\frac{15}{5}\right) ^{\left(1.76-1\right)/1.76 } -1\right)
=\underline{\underline{3299 kJ/kmol} }
Actual work required =\frac{polytropic work}{E_{p} }
=\frac{3299}{0.73} = \underline{\underline{4520 kJ/kmol} }
Power = \frac{4520}{3600} \times 5000=6275 KW
Say,\underline{\underline{6.3 MW} }
T_{2} =288\left(\frac{15}{5} \right) ^{0.4} =\underline{\underline{447 K} }



Related Answered Questions
For the purposes of this calculation it will be su...
The construction of the problem table to find the ...
Component calorific values, from Perry and Chilton...
The rate of heat transfer from the jacket to the w...
Material balance
Basis: 100 kg (as analysis is by ...
As the calculations will be repetitive, use a spre...
From the Mollier diagram, shown diagrammatically i...
Method 1
Using the more general equation 3.26
[lat...