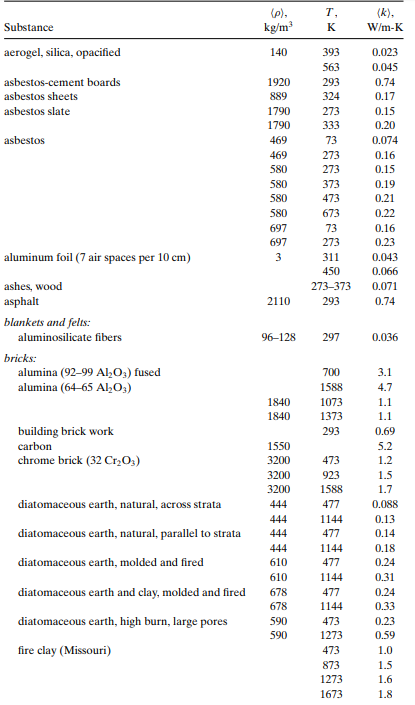
Insulation materials are chosen in part for their mechanical properties. For example, a pipe with free space on its outside is insulated using an insulation wrapping, where this insulation must sustain its weight and in many cases have an outside cover that is impermeable to keep out moisture and reactive gases. In contrast, insulation fillings are (fill-in powders and fill-in foams) added in double-wall pipes or in other confined spaces. These are shown in Figure . Using Table, find (a) a wrapping pipe insulation for use at T = 300 K, (b) a foam formed in place for use at T = 300 K, (c) an insulating cement for use at 450 K, (d) a blanket insulation for use at 300 K, and (e) a mineral powder insulation for use at 1,100 K
Question 3.5: Insulation materials are chosen in part for their mechanical...




The Blue Check Mark means that this solution has been answered and checked by an expert. This guarantees that the final answer is accurate.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
Learn more on how we answer questions.
(a) For a wrapping pipe insulation, from Table , we choose
pipe insulation (slag or glass):
\left\langle\rho \right\rangle =48 t0 64 Kg/m^{3}, T = 297 K, \left\langle k \right\rangle = 0.033 W/m-K.
The denser wrapping \left\langle\rho \right\rangle = 160 to 240 kg/m^{3}, adds strength without much increase in \left\langle k \right\rangle (i.e., \left\langle k \right\rangle = 0.048 W/m-K).
(b) For a foam formed in place, from Table, we choose
polyurethane foam (formed in place):
\left\langle \rho \right\rangle=70 Kg/m^{3}, , T = 300 K, \left\langle k \right\rangle=0.026 W/m-K
There are a variety of foams formed in place and depending on the strength needed, different \left\langle \rho \right\rangle are selected.
(c) For an insulating cement that can be applied as a coating to the outside of a pipe, from Table, we choose
cement (insulating):
\left\langle \rho \right\rangle=380 to 480 Kg/m^{3}, , T = 297 K, \left\langle k \right\rangle=0.071 W/m-K
(d) For a blanket insulation, from Table, we choose
blanket and felt (aluminosilicate fibers):
\left\langle \rho \right\rangle=96 t0 128 Kg/m^{3}, , T = 297 K, \left\langle k \right\rangle=0.036 W/m-K
(e) For a mineral powder insulation, from Table, we choose
diatomaceous-earth powder (coarse):
\left\langle \rho \right\rangle=320 Kg/m^{3}, , T = 1,144 K, \left\langle k \right\rangle=0.062 W/m-K
Note that choosing a higher density will generally increase \left\langle k \right\rangle noticeably



Related Answered Questions
The thermal circuit diagram for the heater node [l...
The transient, uniform temperature of a body of vo...
We assume that the penetration depth is much small...
We assume that the elapsed time of interest is suf...
Because of the thick-layer assumption, the semi-in...
(a) To determine the temperature at the center of ...
The maximum cooling power is given by Q_{c...
Using (\dot{S}_{e,p})_{c}=-\alpha _{s}J_{e...
(a) The physical model of the problem is that show...
Since we have assumed a negligible temperature and...