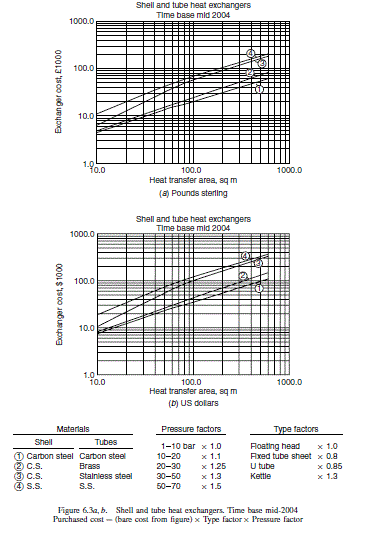
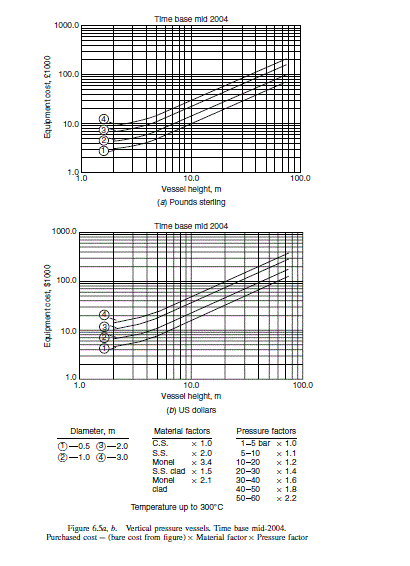
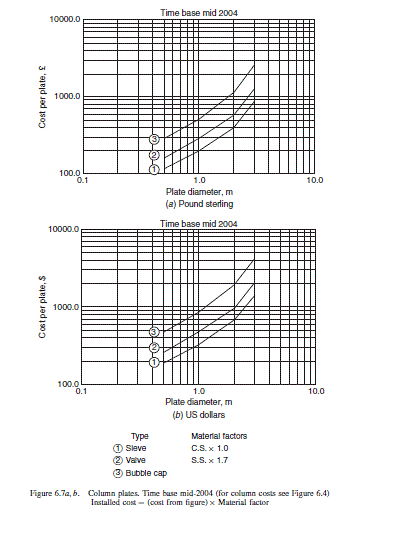
Purchased cost of major equipment items.
Absorption column
Bare vessel cost (Figure 6.5a) £21,000; material factor 1.0, pressure factor 1.1
\text { Vessel cost }=21,000 \times 1.0 \times 1.1=£ 23,000
Packing cost (Table 6.3) £840/ m^{3}
| Table 6.3. Cost of column packing. Cost basis mid 2004 |
|
Cost |
£ / m^{3}\left(\$ / m^{3}\right) |
| Size, mm |
25 |
38 |
50 |
| Saddles, stoneware |
840 (1400) |
620 (1020) |
580 (960) |
| Pall rings, polypropylene |
650 (1080) |
400 (650) |
250 (400) |
| Pall rings, stainless steel |
1500 (2500) |
1500 (2500) |
830 (1360) |
\text { Volume of packing }=(\pi / 4) \times 12=9.4 m ^{3}
\text { Cost of column packing }=9.4 \times 840=£ 7896
Total cost of column 21,000 + 7896 = 28,896, say £29,000
Recovery column
Bare vessel cost (Figure 6.5a) £26,000; material factor 2.0, pressure factor 1.0
\text { Vessel cost } 26,000 \times 2.0 \times 1.0=£ 52,000
Cost of a plate (Figure 6.7a), material factor 1.7 = 200 \times 1.7 = £340
Total cost of plates = 35 \times 340 = £11,900
Total cost of column = 52,000 + 11,900 = 63,900, say £64,000
Reboiler
Bare cost (Figure 6.3a) £11,000; type factor 0.8, pressure factor 1.0
\text { Purchased cost }=11,000 \times 0.8 \times 1.0=£ 8800
Condenser
Bare cost (Figure 6.3a) £8500; type factor 0.8, pressure factor 1.0
\text { Purchased cost }=8500 \times 0.8 \times 1.0=£ 6800
Cooler
Bare cost (Figure 6.3a) £4300; type factor 0.85, pressure factor 1.0
\text { Purchased cost }=4300 \times 0.85 \times 1.0=£ 3700
Solvent tank
\text { Purchase cost }(\text { Table } 6.2)=1400 \times(35)^{0.55}=£ 9894 \text {, say } £ 10,000
| Table 6.2. Purchase cost of miscellaneous equipment, cost factors for use in equation 6.7. Cost basis mid 2004 |
| Equipment |
Size unit, S |
Size range |
Constant |
Index n |
Comment |
| C,£ |
C,$ |
| Agitators |
|
| Propeller |
driver |
5-75 |
1200 |
1900 |
0.5 |
|
| Turbine |
power, kW |
1800 |
3000 |
0.5 |
| Boilers |
|
| Packaged |
|
oil or gas fired |
| up to 10 bar |
kg/h steam |
(5-50) \times 10^{3} |
70 |
120 |
0.8 |
|
| 10 to 60 bar |
|
60 |
100 |
0.8 |
| Centrifuges |
|
| Horizontal basket |
dia., m |
0.5-1.0 |
35,000 |
58,000 |
1.3 |
carbon steel |
| Vertical basket |
|
35,000 |
58,000 |
1 |
\times 1.7 \text { for ss } |
| Compressors |
|
| Centrifugal |
driver |
20-500 |
1160 |
1920 |
0.8 |
electric, |
|
power, kW |
|
max. press. |
| Reciprocating |
|
1600 |
2700 |
0.8 |
50 bar |
| Conveyors |
length, m |
|
| Belt |
|
2-40 |
1200 |
1900 |
0.75 |
|
| 0.5 m wide |
|
1800 |
2900 |
0.75 |
| 1.0 m wide |
|
| Crushers |
t/h |
|
| Cone |
kg/h |
20-200 |
2300 |
3800 |
0.85 |
|
| Pulverisers |
|
2000 |
3400 |
0.35 |
| Dryers |
\text { area, } m ^{2} |
|
|
| Rotary |
|
5-30 |
21,000 |
35,000 |
0.45 |
direct |
| Pan |
2-10 |
4700 |
7700 |
0.35 |
gas fired |
| Evaporators |
\text { area, } m ^{2} |
|
| Vertical tube |
|
10-100 |
12,000 |
20,000 |
0.53 |
carbon steel |
| Falling film |
|
6500 |
10,000 |
0.52 |
|
| Filters |
\text { area, } m ^{2} |
|
| Plate and frame |
|
5-50 |
5400 |
8800 |
0.6 |
cast iron |
| Vacuum drum |
1-10 |
21,000 |
34,000 |
0.6 |
carbon steel |
| Furnaces |
|
| Process |
heat abs, kW |
|
| Cylindrical |
|
10^{3}-10^{4} |
330 |
540 |
0.77 |
carbon steel |
| Box |
10^{3}-10^{5} |
340 |
560 |
0.77 |
\times 2.0 ss |
| Reactors |
\text { capacity, } m ^{3} |
|
| Jacketed, |
|
3-30 |
9300 |
15,000 |
0.4 |
carbon steel |
| agitated |
|
18,500 |
31,000 |
0.45 |
glass lined |
| Tanks |
\text { capacity, } m ^{3} |
|
| Process |
|
2400 |
0.6 |
atmos. press. |
| vertical |
|
1-50 |
1450 |
2900 |
0.6 |
carbon steel |
| horizontal |
10-100 |
1750 |
|
| Storage |
|
| floating roof |
|
50-8000 |
2500 |
4350 |
0.55 |
\times 2 \text { for } |
| cone roof |
50-8000 |
1400 |
2300 |
0.55 |
stainless |
Product tank
Purchase cost same as solvent tank = £10,000
Total purchase cost of major equipment items (PCE)
Absorption column 29,000
Recovery column 64,000
Reboiler 8000
Condenser 6000
Cooler 3000
Solvent tank 10,000
Product tank 10,000
Total £130,000
Estimation of fixed capital cost, reference Table 6.1, fluids processing plant:
| Table 6.1. Typical factors for estimation of project fixed capital cost |
| Item |
Process type |
| Fluids |
Fluids- solids |
Solids |
| 1. Major equipment, total purchase |
|
| cost |
PCE |
PCE |
PCE |
| f_{1} Equipment erection 0.4 0.45 0.50 |
0.40 |
0.45 |
0.50 |
| f_{2} Piping |
0.70 |
0.45 |
0.20 |
| f_{3} Instrumentation |
0.20 |
0.15 |
0.10 |
| f_{4} Electrical |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
| f_{5} Buildings, process 0.15 0.10 0.05 |
0.15 |
0.10 |
0.05 |
| * f_{6} Utilities |
0.50 |
0.45 |
0.25 |
| * f_{7} Storages |
0.15 |
0.20 |
0.25 |
| * f_{8} Site development |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
| * f_{9} Ancillary buildings |
0.15 |
0.20 |
0.30 |
| 2. Total physical plant cost (PPC) |
|
| \begin{array}{r} PPC = PCE \left(1+f_{1}+\cdots+f_{9}\right) \\= PCE \times\end{array} |
3.40 |
3.15 |
2.80 |
| f_{10} Design and Engineering |
0.30 |
0.25 |
0.20 |
| f_{11} Contractor’s fee |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
| f_{12} Contingency |
0.10 |
0.10 |
0.10 |
| Fixed capital =317,520(1+0.3+0.1)=44,528 \text { round up to } £ 4445,000 |
1.45 |
1.40 |
1.35 |
\text { *Omitted } for minor extensions or additions to existing sites.
| PCE £130,000 |
_ |
| f_{1} Equipment erection |
0.40 |
| f_{2} Piping |
0.70 |
| f_{3} Instrumentation |
0.20 |
| f_{4} Electrical |
0.10 |
| f_{5} Buildings |
none required |
| f_{6} Utilities |
not applicable |
| f_{7} Storages |
provided in PCE |
| f_{8} Site development |
not applicable |
| f_{9} Ancillary buildings |
none required |
\text { Total physical plant cost }( PPC )=132,300(1+0.4+0.7+0.2+0.1)=£ 317,520
| f_{10} Design and Engineering |
0.30 |
| f_{11} Contractor’s Fee |
none (unlikely to be used for a small, plant project) |
| f_{12} Contingencies |
0.10 |
\text { Fixed capital }=317,520(1+0.3+0.1)=44,528 \text { round up to } £ 445,000
Working capital, allow 5% of fixed capital to cover the cost of the initial solvent charge = 445,000 \times 0.05=£ 22,250.
\text { Total investment required for project }=445,000+22,250=467,250 \text {, say } £ 468,000
Annual operating costs, reference Table 6.6:
| Table 6.6. Summary of production costs |
| Variable costs |
|
Typical values |
| 1. Raw materials |
from flow-sheets |
| 2. Miscellaneous materials |
10 per cent of item (5) |
| 3. Utilities |
from flow-sheet |
| 4. Shipping and packaging |
usually negligible |
|
Sub-total A |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| Fixed costs |
|
|
| 5. Maintenance |
5 -10 per cent of fixed capital |
| 6. Operating labour from manning estimates |
from manning estimates |
| 7. Laboratory costs |
20 -23 per cent of 6 |
| 8. Supervision |
20 per cent of item (6) |
| 9. Plant overheads |
50 per cent of item (6) |
| 10. Capital charges |
10 per cent of the fixed capital |
| 11. Insurance |
1 per cent of the fixed capital |
| 12. Local taxes |
2 per cent of the fixed capital |
| 13. Royalties |
1 per cent of the fixed capital |
|
Sub-total B |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| Direct production costs A + B |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| 13. Sales expense |
|
20- 30 per cent of the direct |
| 14. General overheads |
production cost |
| 15. Research and development |
|
|
Sub-total C |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| Annual production cost = A + B + C=D |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| \text { Production cost } € / k g=\frac{\text { Annual production cost }}{\text { Annual production rate }} |
Operating time, allowing for plant attainment =365 \times 0.95=347 d / y , \quad 347 \times 24= 8328 h/y.
Variable costs:
1. Raw materials, solvent make-up =10 \times 347 \times 400 / 1000= £ 1388
2. Miscellaneous materials, 10% of maintenance cost (item 5) = £ 2200
3. Utilities, cost from Table 6.5:
| Table 6.5. Cost of utilities, typical figures mid-2004 |
| Utility |
UK |
USA |
| Mains water (process water) |
60 p/t |
50 c/t |
| Natural gas |
0.4 p/MJ |
0.7 c/MJ |
| Electricity |
1.0 p/MJ |
1.5 c/MJ |
| Fuel oil |
65 £/t |
100 $/t |
| Cooling water (cooling towers) |
1.5 p/t |
1 c/t |
| Chilled water |
5 p/t |
8 c/t |
| Demineralised water |
90 p/t |
90 c/t |
| Steam (from direct fired boilers) |
7 £/t |
12 $/t |
| Compressed air (9 bar) |
0.4 p / m ^{3}( Stp ) |
0.6 c / m ^{3} |
| Instrument air (9 bar) (dry) |
0.6 p / m ^{3}( Stp ) |
1 c / m ^{3} |
| Refrigeration |
1.0 p/MJ |
1.5 c/MJ |
| Nitrogen |
6 p / m ^{3}( Stp ) |
8 c / m ^{3} |
Steam, at 7£/t =7 \times 8328 \times 200 / 1000= £11,659
Cooling water, at 1.5 p/t =(1.5 / 100) \times 8328 \times 5000 / 1000= £ 625
Power, at 1.2 p/MJ =(1.2 / 100) \times 360 \times 347= £ 1499
4. Shipping and packaging not applicable
Variable costs = £17,371
Fixed costs:
5. Maintenance, take as 5% of fixed capital = 445,000 ð 0.05 = £22,250
6. Operating labour, allow one extra man on days. It is unlikely
that one extra man per shift would be needed to operate
this small plant, and one extra per shift would give
a disproportionately high labour cost.
Say, £30,000 per year, allowing for overheads = £30,000
7. Supervision, no additional supervision would be needed
8. Plant overheads, take as 50% of operating labour = £15,000
9. Laboratory, take as 30% of operating labour = £ 9000
10. Capital charges, 6% of fixed capital (bank rate 4%) £26,700
11. Insurance, 1% of fixed capital £ 4450
12. Local taxes neglect
13. Royalties not applicable
Fixed cost = £107,400
Direct production costs = 17,396 + 107,400 = £124,796
14. Sales expense not applicable
15. General overheads not applicable
16. Research and development not applicable
Annual operating cost, rounded = £125,000